Definition: Actual costing is a cost accounting system that uses actual cost, direct-cost rates, and actual qualities used in production to determine the cost of specific products. Usually an actual costing system traces direct costs to a cost object or something that has a measurable cost.
Actual Cost Def
In other words, managers go back to the source of the costs (cost objects) like labor and materials. Managers can analyze how many hours of manufacturing time a product requires to calculate the actual costs of producing that product.
What Does Actual Costing Mean?
Actual costing requires the manufacturer to assign an ever-changing actual cost to each individual component of the manufacturing process (materials, labor and overhead) each time to get an accurate final price. Material costs (amount paid or incurred) are typically acquired from a purchase order or a manufacturing order. Actual Cost means the cost of construction of all of the Acquisition Improvements, as documented by the Developer to the satisfaction of the Local Agency, as certified by the Local Agency Engineer in an Actual Cost Certificate. Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3. Actual Cost The cost a company pays or is paid for a good or service. The actual cost may be more or less than the estimated cost. For example, a car shop may estimate that repairs will cost $700, but the actual cost may in fact be $800. Actual cash value is equal to the replacement cost minus any depreciation (ACV = replacement cost – depreciation). It represents the dollar amount you could expect to receive for the item if you sold it in the marketplace. The issue is that no commitment cost is appearing once the components purchase requisitions are created. Once I post good issue (through MIGO) only the difference between the planned cost and the purchase actual cost appears on the reports as an actual cost.
Here are the typical actual costing system formulas:
Example
Managers can use these formulas to calculate the total production costs. For instance, managers first need to find out how many hours it took the company to produce the product and how much the company is paying its employees per hour. Using the first actual costing formula, these numbers make up the labor portion of the production costs. The same is done for materials. Overhead is a little different.
Since overhead like utility usage is a little difficult to assign to a single product, managers usually make estimates. They estimate how much overhead was used and how long the overhead was used. Using the second actual costing formula, management can determine the indirect productions costs for producing the product. After all the calculations are done, add up the totals and you’ll get the actual cost of producing your product.
After the actual cost is known, management can change the production process in order to meet budget goals.
Contents
In accounting, actual cost means the amount of money that you spent to obtain an asset.3 min read
1. Basics of Actual Cost2. Actual Cost Approach
3. The Meaning of Actual Cost
4. Actual Cost, Manufacturing, and Planning Expenses
5. Actual Cost Example
In accounting, actual cost means the amount of money that you spent to obtain an asset.
Basics of Actual Cost
When you purchase an asset or a product, the total amount of money that you spend on the purchase is your actual cost.
One of the interesting facts about actual cost is that it may not represent the current price of an asset. For instance, actual cost can also mean the past cost of the product or even its historical cost. If you're not familiar with this accounting term, you might wonder if there are any other costs related to a product other than its actual cost.
Actual cost is the total expenditure required to obtain an asset, and can include several different factors:
- The expense invoiced by your supplier.
- The cost to deliver the asset.
- The cost to set up the asset.
- The cost of testing the asset.
In your business's financial statements, an asset's cost will be recorded as a fixed asset. Actual costs of work performed (ACWP) is another way to say actual cost.
Actual Cost Approach
In many cases, businesses use estimates to attempt to determine future costs, which is much different than the actual cost approach. It's actually quite common to combine the actual cost approach and the estimate approach. Blending these approaches allows for the comparison of actual costs to estimated budgeted costs. You can use the variance between these two cost projections to streamline your operations and to make more accurate predictions in the future.
The Meaning of Actual Cost
When discussing managerial accounting, it's important to remember that in addition to actual costs, you will have forecasted costs and budgeted costs. While budgeted costs and forecasted costs are important, they almost never indicate the actual cost of obtaining a product. For example, your company's management may calculate a budget for purchasing a new business asset, but the price you actually pay for this asset likely won't match this budget. When the price of a product increases, it may be possible for your company to receive a discount from a vendor.
Actual Cost, Manufacturing, and Planning Expenses
Actual cost doesn't only apply to purchasing assets. It can also be used for the cost of manufacturing assets.
When you're planning to manufacture a product, you won't know the actual cost until the product has been created. This is because the actual cost of manufacturing reflects all the expenditures needed to create the product, including the cost of raw materials and the price of the manufacturing machinery. There are several steps you will need to complete when you're planning the expense of manufacturing a product. First, you will need to develop a production plan and calculate an estimate of your expenses.
Next, you will need to examine these projected expenses to determine if they will fit into your company's budget. If not, you will need to adjust your production plan to lower your expenses so that they match the budget.
Hopefully, the actual costs of manufacturing will fit into your company's budget. Unfortunately, this is rarely the case, and it can be hard to meet your projected budget. The total you have paid to manufacture your product is the actual cost, and this cost may either be higher or lower than your forecasted or budgeted cost.
Actual Cost Example
Imagine that you have a project that you want completed in no more than a year and that your project has a budget of $100,000. After six months, you've spent $60,000 on your project, which means you have 40 percent of your budget remaining. While examining the progress of your project, you find that it is only 40 percent completed. With these numbers, you can calculate your current actual cost.
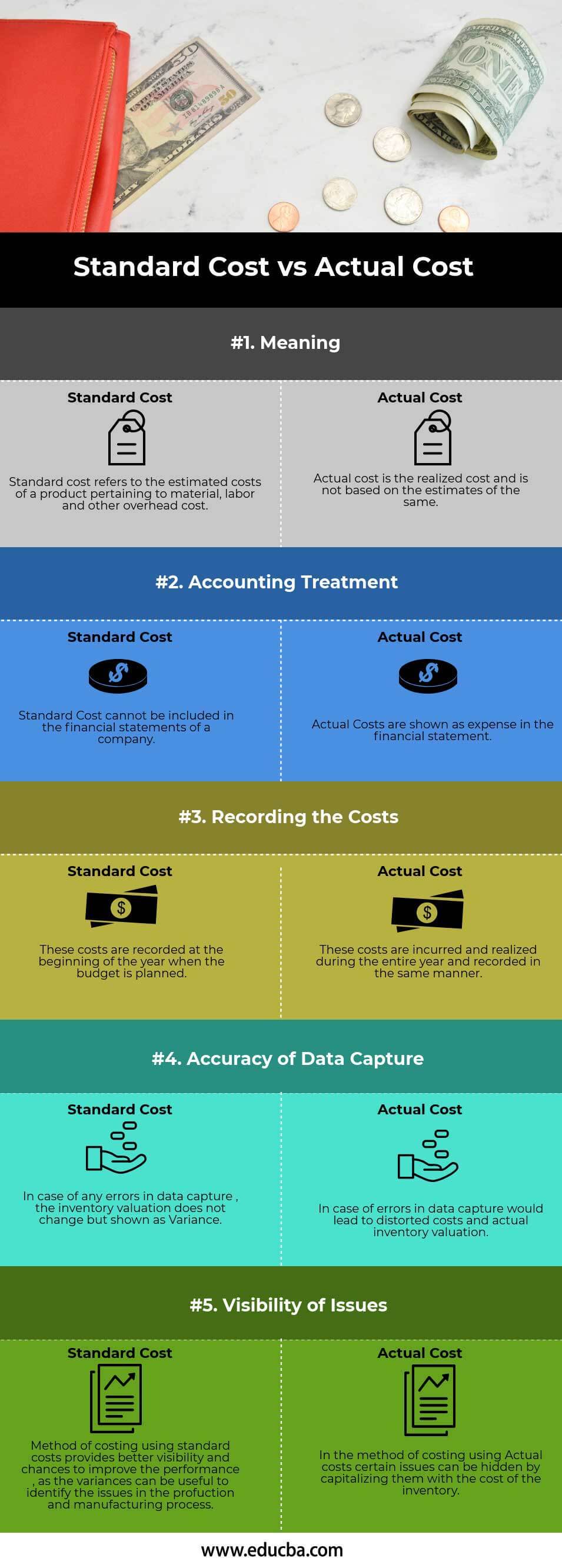
Actual Cost Vs Standard Cost
Actual cost is always the amount that has currently been spent on a project. So, in the above example, your actual cost would be $60,000, since that's what you have already spent. If the project continues and you spend more money, your actual cost will rise. Notice that the actual cost does not reflect how much of the work is complete, only what the work has cost. You can also use actual cost to calculate two indices: Cost Performance and Cost Variance.
Actual Cost To Build A House
If you need help understanding actual cost, you can post your legal needs on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
